I couldn't find a request for this and this would be a really nice plane to add like the L39.
It can be used for combat, training and air displays.
Specifications:BAE SYSTEMS Hawk T.Mk.1
Crew: Two (Instructor – Rear cockpit, Trainee – Front cockpit)
Dimensions: Length 38 ft 11 in (11.86 m) incl. nose probe, 36 ft 7.75 in (11.17 m) excl. nose probe; Height 13 ft 1.24 in (3.99 m); Wing Span 30 ft 9.75 in (9.39 m); Wing Area 179.60 sq ft (16.69 sq m)
Engines: One Rolls-Royce/Turbomeca Adour Mk151-01 rated at 5,200 lb st (23.13 kN) dry
Weights: Empty Equipped 8,040 lb (3647 kg); Normal Take-off 11,100 lb (5035 kg); Maximum Take-off 12,566 lb (5700 kg)
Armament: Normal maximum external ordnance 1,500 lb (680 kg), Absolute maximum external ordnance 6,800 lb (3084 kg) on three hard points. Loads may comprise single 30-mm gun pod under the fuselage, and two AIM-9L Sidewinder air-to-air missiles or light bombs or [Export versions only] two underwing drop tanks of up to 190 Imp gal (228 US gal, 864 litres)
Performance: Maximum level speed 560 kt (645 mph, 1038 km/h) at 11,000 ft (3355 m); Maximum rate of climb at sea level 9,300 ft/min (2835 m/min); Service ceiling 50,000 ft (15240 m); Standard range 1310 nm (1509 miles, 2428 km); Ferry range 1670 nm (1923 miles, 3094 km)Basic info:The Hawk originates from a 1964 requirement for a new RAF trainer to replace the Gnat. The two-seat Jaguar was initially intended for this role, but it was soon realised that this would be far from ideal. Accordingly, in 1968 Hawker Siddeley Aviation began the design of a much simpler strictly subsonic trainer, which it designated P.1182 (later HS.1182). The stepped cockpit, allowing the instructor in the rear seat a good forward view, was an innovation subsequently adopted by many other training aircraft.
Confidence in the design was such that no prototypes or pre-production aircraft were ordered, the first six production aircraft being used for development testing. Five of these aircraft were later delivered to the RAF. After entering RAF service in April 1976, the Hawk replaced the Gnat and Hunter in the advanced training and weapons training roles respectively. The most famous RAF operator being the ‘Red Arrows’ aerobatic team.
The Hawk gained an additional role from January 1983, when modification of 88 RAF aircraft to carry Sidewinder missiles commenced. The resulting T.Mk 1A variant was intended for emergency use as a point-defence fighter, supporting Phantoms and Tornados in the UK Defence Region. These aircraft are now used as dedicated weapons trainers. The Hawk subsequently replaced the Canberra in the target towing role.
The Royal Navy also acquired a dozen Hawk T.Mk 1/1As from the RAF, for use by FRADU as aerial targets for the training of ships gunners and radar operators.
From an early stage, the Hawk had aroused considerable export interest, and in 1977 the 50 series export variant was introduced. This minimum change version included provision for underwing drop tanks for the first time. In 1982 an improved export version, the 60 series was introduced, featuring an uprated engine, improved wing aerodynamics and revised wheels and tyres. Further development led to the Hawk 100 and Hawk 200 series, described separately. The T-45 Goshawk variant, adopted by the US Navy is also described separately.Varients:P.1182 Designation for initial project studies
HS.1182 Manufacturers designation for final project studies
Hawk T.Mk 1 Initial production version. No prototypes or pre-production aircraft produced
Hawk T.Mk 1A Modification to T.Mk 1A to allow installation of AIM-9L Sidewinder AAMs on underwing launchers for use in a back-up air defence role
Hawk 50 series Initial export version based on T.Mk 1
Hawk Mk 51 Initial export version for Finland
Hawk Mk 51A Second export batch for Finland
Hawk Mk 52 Export version for Kenya
Hawk Mk 53 Export version for Indonesia
Hawk 60 series Improved export version. Uprated Mk 861 Adour engine of 5,700 lb st (25.4 kN), additional wing leading-edge fences and four-position flaps to improve lift, anti-skid brakes and revised wheels and tyres.
Hawk Mk 60 Initial 60 series export version
Hawk Mk 60A Second batch for Indonesia
Hawk Mk 61 Export version for Dubai
Hawk Mk 63 Upgrade conversion of Mk 60 for Abu Dhabi
Hawk Mk 64 Export version for Kuwait
Hawk Mk 65 Export version for Saudi Arabia
Hawk Mk 66 Export version for Switzerland
Hawk Mk 67 Hybrid export version for South Korea. Combines a 60 series airframe with the avionics and systems of the 100 series aircraft. Equipped with ranging radar in an extended nose and nosewheel steering.
Hawk 100 series Advanced two-seat trainer and light attack variant
Hawk 200 series Single-seat fighter and ground attack variant
T-45 Goshawk Carrier-landing capable variant for the US NavyIMAGESBlueprints: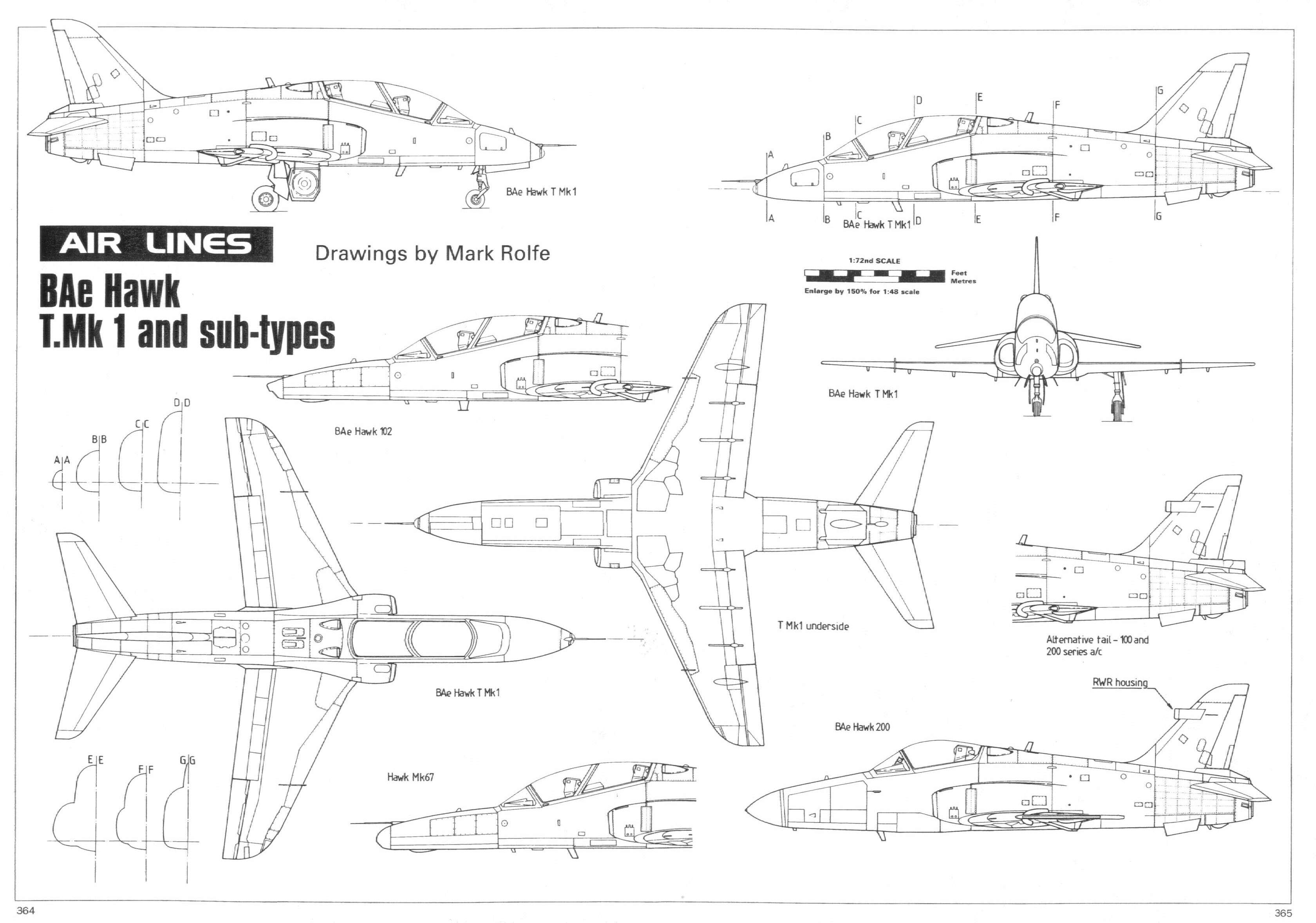
 Cockpit:
Cockpit:
 General photos
General photos


 Author
Topic: BAE systems Hawk. (Read 10570 times)
Author
Topic: BAE systems Hawk. (Read 10570 times)


