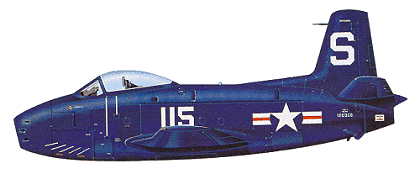
North American FJ-1 FuryThe North American FJ-1 Fury was the first operational jet aircraft in United States Navy service, and was developed by North American Aviation as the NA-135. The FJ-1 was an early transitional jet of limited success which carried over similar tail surfaces, wing and canopy derived from the piston-engined P-51D Mustang. The evolution of the design to incorporate swept wings would become the basis for the land-based XP-86 prototype - itself originally designed with a very similar straight-wing planform to the FJ-1 airframe - of the United States Air Force's enormously influential F-86 Sabre, which itself formed the basis for the Navy's carrier-based North American FJ-2/-3 Fury.
Design and Development Ordered in late 1944 as the XFJ-1 in competition with proposals from Douglas and Vought, the Fury began as a straight-wing, tricycle gear fighter with a single turbojet passing through the fuselage. The wing, empennage and canopy strongly resembled that of the piston-engined P-51D Mustang, North American Aviation's highly successful World War II fighter.
Operational HistoryThe first flight of the prototype XFJ-1 took place on 11 September 1946, with the first of 30 deliveries beginning in October 1947. Flown by Navy squadron VF-5A, the FJ-1 made the USN's first operational aircraft carrier landing with a jet fighter at sea on 10 March 1948 aboard USS Boxer, pioneering US jet-powered carrier operations and underscoring the need for catapult-equipped carriers. The Fury was capable of launching without catapult assistance, but on a crowded flight deck the capability was of limited use. Taking off without a catapult launch limited the FJ-1 to a perilous, slow climb that was considered too risky for normal operations.
As German research into swept wing aerodynamics was not yet available when the design was finalized, the FJ-1 used a straight wing. No provision for wing-folding had been made as dive brakes mounted in the wings made that option unfeasible. In order to conserve carrier deck space, a unique "kneeling" nose undercarriage along with a swivelling "jockey wheel" allowed the FJ-1 to be stacked tail-high, close to another FJ-1.
Although ordered into production, the initial order for 100 units was trimmed to only 30 aircraft which were mainly used in testing at NAS North Island, California. VF-5A, soon redesignated as VF-51, operated the type in service beginning in August 1948. Although VF-51 went to sea on Boxer by May 1949, the FJ-1s were phased out in favor of the new F9F-2 Panther.
Ending its service career in U.S. Naval Reserve units, the FJ-1 eventually was retired in 1953. The one highlight in its short service life was VF-51's win in the Bendix Trophy Race for jets in September 1948. The unit entered seven FJ-1s, flying from Long Beach, California to Cleveland, Ohio, with VF-51 aircraft taking the first four places, ahead of two California Air National Guard Lockheed F-80 Shooting Stars.
VarientsXFJ-1Prototype aircraft, powered by a 3,820 lbf (17 kN) General Electric J35-GE-2 turbojet engine, three built.
FJ-1 FurySingle-seat fighter aircraft, powered by a 4,000 lbf (17.8 kN) Allison J35-A-2 turbojet engine, armed with six 0.50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns, 30 built.
SpecificationsGeneral characteristics
Crew: 1
Length: 34 ft 5 in (10.48 m)
Wingspan: 38 ft 2 in (11.63 m)
Height: 14 ft 10 in (4.52 m)
Wing area: 221 ft² (20.5 m²)
Empty weight: 8,843 lb (4,010 kg)
Loaded weight: 15,118 lb (6,854 kg)
Powerplant: 1 × Allison J35-A-2 turbojet, 4,000 lbf (17.8 kN)
Fuel provisions Internal fuel load: 465 gal (1,743 l), Wing Tip Tanks: 2 × 170 gal (644 l)
Performance
Maximum speed: 547 mph at 9,000 ft (880 km/h at 2,743 m)
Range: 1,496 mi, (2,407 km) 1,496 mi (2,407 km) with external tanks
Service ceiling: 32,000 ft. (9,753 m)
Rate of climb: 3,300 ft/min at sea level (1,005 m/min)
Thrust/weight: 0.38
Stalling speed (power off): 121 mph (106 kn, 194 km/h)
Armament
Guns: 6 × 0.50 in (12.7 mm) M2 Browning machine guns (1,500 rounds in total)
Pictures and Illustrations 


_1948.jpeg)






 Author
Topic: North American FJ-1 Fury (Read 7576 times)
Author
Topic: North American FJ-1 Fury (Read 7576 times)


